Understanding Accounting Fraud and Cybersecurity Risks
- Unmasking the Hidden Threat: An Overview of Accounting Fraud
- What Is Accounting Fraud? A Deceptive Practice Defined
- Types of Accounting Fraud
- Traditional vs. Modern Methods of Accounting Fraud
- The Impact of Accounting Fraud on Businesses
- Bridging the Gap: The Intersection of Accounting Fraud and Cybersecurity
- How Digitalization Has Transformed Accounting Fraud
- The Digital Shift in Fraud Tactics
- Common Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities Exploited in Accounting Fraud
- Key Vulnerabilities Leading to Accounting Fraud
- Real-World Insights: Case Studies of Major Accounting Fraud Incidents Related to Cybersecurity
- Case Study 1: The Infamous Wirecard Scandal
- Case Study 2: The Equifax Breach and Its Financial Fallout
- Case Study 3: The Tesco Bank Fraud Incident
- Fortifying Your Defenses: Cybersecurity Measures to Prevent Accounting Fraud
- The Power of Encryption: Securing Data at Its Core
- Multi-Factor Authentication: A Stronger Barrier Against Fraud
- The Human Element: Employee Training and Awareness in Cybersecurity
- Swift Action: Responding to Accounting Fraud Incidents
- Immediate Steps: What to Do When Accounting Fraud Is Detected
- Crafting a Targeted Response: Incident Response Plans for Accounting Fraud
- Navigating the Legal Landscape: Regulatory Considerations in Accounting Fraud Response
- Looking Ahead: Future Trends in Accounting Fraud and Cybersecurity
- Emerging Threats in the Digital Landscape
- The Evolving Role of Cybersecurity in Accounting
- Predictions for the Future of Accounting Fraud Prevention
- Defending Against Deception: SearchInform’s Solutions for Combating Accounting Fraud
- Proactive Monitoring with SearchInform’s DLP Solutions
- Strengthening Incident Detection and Response
- Enhancing Network Security for Financial Data
- Comprehensive Risk Management and Compliance
- The Future of Fraud Prevention with SearchInform
Unmasking the Hidden Threat: An Overview of Accounting Fraud
In previous sections, we've delved into various forms of fraud that can plague organizations, from financial statement fraud to cybersecurity breaches. Now, we turn our attention to a more insidious threat—accounting fraud. This form of fraud can quietly erode the financial foundation of a company, leading to devastating consequences. Understanding accounting fraud is crucial for businesses aiming to safeguard their assets and maintain trust with stakeholders.
What Is Accounting Fraud? A Deceptive Practice Defined
Accounting fraud refers to the deliberate manipulation or falsification of financial statements or accounting records to present a false picture of a company's financial health. This type of fraud can be executed by individuals within an organization, such as employees, managers, or executives, and sometimes in collusion with external parties like auditors or consultants.
Types of Accounting Fraud
Accounting fraud can manifest in various forms, each with its own methods and motivations:
- Falsification of financial statements: Manipulating earnings reports, balance sheets, or cash flow statements to inflate profits, understate liabilities, or hide losses.
- Revenue recognition fraud: Recording revenue before it is actually earned or recognized, often to meet financial targets or secure bonuses.
- Expense fraud: Underreporting expenses or inflating assets to present a healthier financial position.
- Misappropriation of assets: Theft or misuse of company resources, disguised within financial records to avoid detection.
Traditional vs. Modern Methods of Accounting Fraud
Accounting fraud has evolved over the years, adapting to new technologies and regulatory environments. Traditional methods often involved manual record-keeping and physical document tampering, making detection a painstaking and time-consuming process.
However, in the modern era, fraudsters have become more sophisticated, leveraging digital tools to conceal their actions. Today, accounting fraud might involve complex schemes like:
- Digital manipulation of financial records: Using software to alter or fabricate accounting entries without leaving a paper trail.
- Cyber fraud and hacking: Gaining unauthorized access to financial systems to modify or destroy records.
- Collusion with external auditors: Partnering with complicit auditors to overlook discrepancies during audits.
The Impact of Accounting Fraud on Businesses
The repercussions of accounting fraud are far-reaching, impacting not only the financial health of a business but also its reputation, operational stability, and legal standing. Here’s how accounting fraud can harm a company:
- Financial loss: Fraudulent activities can result in significant monetary losses, affecting cash flow, profitability, and overall financial stability.
- Legal consequences: Businesses involved in accounting fraud may face severe penalties, including fines, sanctions, and even criminal charges against responsible individuals.
- Damage to reputation: The revelation of accounting fraud can erode stakeholder trust, leading to a loss of customers, investors, and business partners.
- Operational disruption: Investigations and legal proceedings stemming from accounting fraud can disrupt daily operations, diverting resources and attention away from core business activities.
Understanding the various facets of accounting fraud and its impact is essential for businesses striving to protect their financial integrity. In the next sections, we will explore the strategies and tools that can be employed to detect and prevent accounting fraud, ensuring that organizations remain vigilant against this ever-present threat.
Bridging the Gap: The Intersection of Accounting Fraud and Cybersecurity
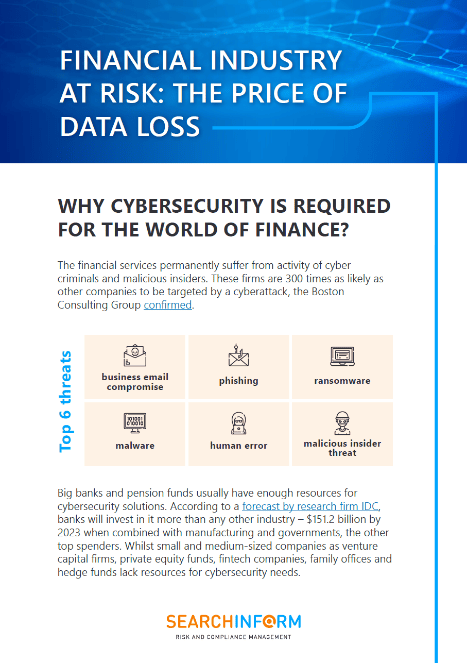
As we have explored in previous chapters, accounting fraud remains a significant threat to organizations across various industries. However, in today's rapidly digitalizing world, the convergence of accounting fraud and cybersecurity has created new challenges for businesses. The digital landscape, while offering unprecedented opportunities for growth, has also opened up avenues for fraudsters to exploit vulnerabilities. Understanding the intersection of accounting fraud and cybersecurity is now more critical than ever for organizations aiming to protect their financial integrity.
How Digitalization Has Transformed Accounting Fraud
The digital revolution has fundamentally altered how businesses operate, bringing both advantages and risks. While automation and data analytics have streamlined financial processes, they have also introduced new opportunities for accounting fraud. In the past, accounting fraud was primarily manual, involving physical tampering with financial records. Today, fraudsters have adapted to digital tools, making their schemes more sophisticated and harder to detect.
The Digital Shift in Fraud Tactics
Accounting fraud in the digital age often involves the manipulation of electronic records, unauthorized access to financial systems, and the exploitation of complex software vulnerabilities. For example, fraudsters may use advanced techniques to alter accounting software data, creating fictitious transactions or concealing illicit activities. These digital manipulations are difficult to trace, especially if the organization's cybersecurity measures are not robust.
Moreover, the integration of cloud computing and remote access technologies has expanded the attack surface for cybercriminals. The convenience of accessing financial systems from anywhere in the world also means that unauthorized individuals can exploit these systems if proper cybersecurity measures are not in place. As a result, the digitalization of financial processes has not only changed the methods of accounting fraud but has also amplified its potential impact.
Common Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities Exploited in Accounting Fraud
At the heart of the intersection between accounting fraud and cybersecurity lies the exploitation of vulnerabilities within an organization’s digital infrastructure. These vulnerabilities can stem from various sources, including outdated software, inadequate access controls, and poor employee training on cybersecurity best practices.
Key Vulnerabilities Leading to Accounting Fraud
- Weak Password Policies: Simple or reused passwords are a gateway for fraudsters to gain unauthorized access to financial systems, allowing them to alter records or initiate fraudulent transactions.
- Insufficient Access Controls: Without strict access controls, employees may have more permissions than necessary, increasing the risk of internal fraud or external breaches.
- Outdated Software: Legacy systems or unpatched software can harbor known vulnerabilities that fraudsters exploit to infiltrate financial databases.
- Lack of Employee Awareness: Employees who are not trained in recognizing phishing attempts or other cybersecurity threats can inadvertently expose sensitive financial information, leading to accounting fraud.
Real-World Insights: Case Studies of Major Accounting Fraud Incidents Related to Cybersecurity
To fully grasp the severity of accounting fraud in the digital age, it is essential to examine real-world examples where cybersecurity lapses have facilitated fraudulent activities. These case studies highlight the intricate relationship between accounting fraud and cybersecurity, demonstrating how one often feeds into the other.
Case Study 1: The Infamous Wirecard Scandal
One of the most notorious cases of accounting fraud in recent years is the Wirecard scandal, where the German payment processing company was found to have inflated its balance sheet by €1.9 billion. This massive fraud was facilitated by sophisticated cyber tactics, including the manipulation of financial software and the exploitation of gaps in cybersecurity protocols. The scandal not only led to the company’s collapse but also exposed significant vulnerabilities in regulatory oversight and corporate governance.
Case Study 2: The Equifax Breach and Its Financial Fallout
Another significant incident was the Equifax data breach, which, while primarily a cybersecurity breach, had far-reaching implications for accounting and financial reporting. Hackers exploited a vulnerability in Equifax's software, gaining access to sensitive financial data of over 147 million customers. The breach led to widespread financial fraud, including the manipulation of credit reports and identity theft, ultimately causing substantial financial losses and legal penalties for the company.
Case Study 3: The Tesco Bank Fraud Incident
In 2016, Tesco Bank in the UK experienced a cyber attack that resulted in fraudulent transactions affecting over 9,000 customer accounts. The fraudsters exploited vulnerabilities in the bank’s online banking system, demonstrating how inadequate cybersecurity measures can lead to direct financial losses. While not a traditional case of accounting fraud, this incident underscores how cyber vulnerabilities can be leveraged to execute fraud that affects a company’s financial standing.
These case studies illustrate the devastating impact of accounting fraud facilitated by cybersecurity weaknesses. They serve as a stark reminder that in the digital era, the line between accounting fraud and cybersecurity is increasingly blurred.
As businesses continue to embrace digitalization, the importance of integrating robust cybersecurity measures into financial processes cannot be overstated. In the upcoming sections, we will explore strategies for strengthening cybersecurity to prevent accounting fraud, ensuring that organizations remain resilient in the face of these evolving threats.
Fortifying Your Defenses: Cybersecurity Measures to Prevent Accounting Fraud
As we explored in the previous sections, accounting fraud has evolved with the rise of digitalization, creating new challenges for businesses. The intersection of accounting fraud and cybersecurity has become a critical battleground where companies must be vigilant. Preventing accounting fraud in this digital age requires implementing robust cybersecurity measures that go beyond traditional practices. Let’s delve into some key strategies that can help safeguard your organization against this pervasive threat.
The Power of Encryption: Securing Data at Its Core
In today’s digital landscape, encryption stands as a vital defense mechanism against accounting fraud. By converting sensitive financial data into unreadable code, encryption ensures that even if unauthorized individuals gain access to this information, they cannot decipher it without the correct decryption keys. This layer of security is particularly crucial for organizations handling large volumes of financial transactions and records, as it protects against data breaches and unauthorized access.
Why Encryption Matters:
- Data Integrity: Encryption helps maintain the integrity of financial data by preventing unauthorized alterations, ensuring that records remain accurate and reliable.
- Compliance: Many regulatory frameworks require the use of encryption to protect sensitive financial information, making it an essential component of compliance efforts.
- Risk Mitigation: In the event of a cyber attack, encrypted data is significantly less valuable to attackers, reducing the potential damage and financial loss.
Implementing encryption across all financial systems and communications is a fundamental step in protecting against accounting fraud. However, encryption alone is not enough. It must be part of a broader, multi-layered cybersecurity strategy.
Multi-Factor Authentication: A Stronger Barrier Against Fraud
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) has emerged as one of the most effective tools in the fight against accounting fraud. By requiring users to provide two or more verification factors before accessing financial systems, MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. This added layer of security is especially important in protecting against fraudsters who might have obtained login credentials through phishing or other malicious means.
The Role of MFA in Fraud Prevention:
- Enhanced Security: MFA ensures that even if one authentication factor (such as a password) is compromised, additional factors (such as a fingerprint or a security token) provide a critical line of defense.
- Reduced Insider Threats: By limiting access to sensitive financial systems, MFA helps prevent employees from engaging in fraudulent activities or accessing information they are not authorized to view.
- Adaptability: MFA can be tailored to fit the needs of different organizations, with options ranging from simple SMS verification to more advanced biometric authentication.
Incorporating MFA into your organization’s cybersecurity framework is a powerful way to bolster defenses against accounting fraud. It not only protects financial data but also builds trust with stakeholders by demonstrating a commitment to security.
The Human Element: Employee Training and Awareness in Cybersecurity
While technology plays a significant role in preventing accounting fraud, the human element cannot be overlooked. Employees are often the first line of defense against cyber threats, and their awareness and vigilance are crucial in identifying and mitigating risks. Comprehensive cybersecurity training programs are essential for educating employees about the dangers of accounting fraud and the best practices for preventing it.
Key Components of Effective Employee Training:
- Phishing Awareness: Training employees to recognize phishing attempts can prevent fraudsters from gaining access to financial systems through deceptive emails or links.
- Password Management: Educating employees on the importance of strong, unique passwords and the dangers of password reuse can help prevent unauthorized access.
- Incident Reporting: Establishing clear protocols for reporting suspicious activities ensures that potential threats are addressed promptly, minimizing the risk of accounting fraud.
- Ongoing Education: Cybersecurity threats are constantly evolving, and so should employee training. Regular updates and refresher courses keep employees informed about the latest risks and defenses.
A well-trained workforce is one of the most effective tools in preventing accounting fraud. When employees understand the importance of cybersecurity and their role in maintaining it, they become active participants in protecting the organization’s financial integrity.
By combining encryption, multi-factor authentication, and comprehensive employee training, organizations can create a robust defense system against accounting fraud. These measures, when implemented together, form a multi-layered approach that addresses both technological and human vulnerabilities.
Swift Action: Responding to Accounting Fraud Incidents
In our previous discussions, we've highlighted the critical role of cybersecurity measures in preventing accounting fraud. However, even the most robust defenses can sometimes be breached. When accounting fraud is detected, how an organization responds can make all the difference in minimizing damage and preserving trust. Understanding the essential steps and legal considerations involved in responding to accounting fraud incidents is crucial for effective crisis management.
Immediate Steps: What to Do When Accounting Fraud Is Detected
The discovery of accounting fraud can send shockwaves through an organization, but it’s vital to act swiftly and decisively. The initial response to an accounting fraud incident can significantly impact the outcome, from limiting financial losses to safeguarding the organization’s reputation.
Key Steps to Take Upon Detection:
- Contain the Situation: The first priority is to prevent further fraudulent activities. This may involve restricting access to financial systems, freezing suspicious accounts, or halting certain transactions until a thorough investigation is conducted.
- Preserve Evidence: It’s essential to secure all relevant data and documentation related to the suspected fraud. This includes accounting records, emails, transaction logs, and any other digital or physical evidence that could be pertinent to the investigation. Preserving evidence is crucial for both internal investigations and potential legal proceedings.
- Notify Key Stakeholders: Informing senior management, the board of directors, and, if necessary, legal counsel about the incident is a critical early step. Transparency with internal stakeholders ensures that appropriate resources are allocated for the investigation and response efforts.
- Initiate an Internal Investigation: An internal investigation should be launched immediately to assess the scope and impact of the accounting fraud. This may involve forensic accountants, IT specialists, and legal advisors who can work together to uncover the details of the fraudulent activities.
Crafting a Targeted Response: Incident Response Plans for Accounting Fraud
Every organization should have an incident response plan tailored specifically to accounting fraud. This plan serves as a roadmap for addressing fraud incidents, ensuring that all necessary actions are taken in a timely and organized manner. A well-crafted incident response plan not only mitigates the impact of fraud but also strengthens the organization’s resilience against future threats.
Components of an Effective Incident Response Plan:
- Defined Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly outline the roles and responsibilities of each team member involved in the response, from IT and finance to legal and communications. This ensures a coordinated effort and prevents confusion during a crisis.
- Communication Protocols: Establish clear lines of communication both internally and externally. This includes how and when to inform stakeholders, regulators, and, if necessary, the public. Maintaining control over the narrative is crucial in minimizing reputational damage.
- Investigation Procedures: Detail the steps for conducting a thorough investigation, including data collection, interviews, and analysis. The plan should also specify the criteria for involving external experts or law enforcement if the situation warrants it.
- Recovery and Remediation: Outline the actions needed to recover from the fraud incident, such as restoring affected systems, addressing financial losses, and implementing corrective measures to prevent future occurrences. This might also include revisiting and strengthening internal controls and cybersecurity protocols.
Navigating the Legal Landscape: Regulatory Considerations in Accounting Fraud Response
Responding to accounting fraud involves navigating a complex web of legal and regulatory requirements. Failure to comply with these obligations can result in severe penalties and further damage to the organization’s reputation. Understanding the legal landscape is essential for a comprehensive response.
Key Legal and Regulatory Considerations:
- Compliance with Reporting Requirements: Depending on the jurisdiction and industry, organizations may be legally required to report instances of accounting fraud to regulatory bodies. This could include financial regulators, stock exchanges, or industry-specific oversight agencies. Prompt and accurate reporting is critical to avoid additional penalties.
- Data Privacy Regulations: If the accounting fraud involves the unauthorized access or exposure of sensitive financial data, organizations must comply with data privacy laws such as the GDPR or CCPA. This includes notifying affected parties and taking steps to mitigate any data breaches.
- Legal Action and Litigation: In some cases, organizations may need to pursue legal action against the perpetrators of the fraud. This could involve civil litigation to recover stolen assets or criminal charges for those responsible. It’s also important to be prepared for potential lawsuits from affected stakeholders, such as investors or customers.
- Regulatory Audits and Inquiries: Following an accounting fraud incident, organizations may be subject to regulatory audits or inquiries. Being prepared to cooperate fully with regulators and provide all necessary documentation can help mitigate the consequences of the fraud.
In the aftermath of an accounting fraud incident, the steps taken by an organization are critical to its recovery. By following a structured response plan and adhering to legal requirements, businesses can navigate the complexities of fraud incidents while minimizing damage and rebuilding trust.
Looking Ahead: Future Trends in Accounting Fraud and Cybersecurity
As we've discussed, accounting fraud has become increasingly sophisticated with the rise of digital technologies, making it a formidable challenge for businesses worldwide. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, so too do the threats and the necessary defenses against accounting fraud. Understanding the future trends in accounting fraud and cybersecurity is essential for organizations striving to stay ahead of potential risks and protect their financial integrity.
Emerging Threats in the Digital Landscape
The digital age has ushered in a new era of innovation, but it has also created fertile ground for emerging threats that could significantly impact accounting fraud. These threats are becoming more advanced, leveraging cutting-edge technologies to bypass traditional security measures.
Key Emerging Threats:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Fraud: While AI is often seen as a tool for fraud detection, it is also being harnessed by fraudsters to automate and enhance their schemes. AI-driven accounting fraud could involve the creation of highly sophisticated fake transactions or the manipulation of financial records in ways that are difficult to detect using conventional methods.
- Ransomware Targeting Financial Data: Ransomware attacks are becoming more targeted, with cybercriminals focusing on financial systems and accounting software. By encrypting critical financial data, attackers can demand ransom payments in exchange for restoring access, leaving businesses vulnerable to both financial loss and accounting fraud.
- Blockchain Exploitation: As blockchain technology becomes more integrated into financial systems, it presents both opportunities and risks. While blockchain is touted for its security, fraudsters are exploring ways to exploit vulnerabilities in smart contracts or decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms to commit accounting fraud.
- Social Engineering 2.0: Social engineering tactics are evolving, with fraudsters using more personalized and convincing methods to deceive employees into divulging sensitive financial information. These sophisticated phishing attacks can lead to unauthorized access to accounting systems and subsequent fraud.
As these threats continue to evolve, businesses must remain vigilant and adapt their cybersecurity strategies to address these emerging risks.
The Evolving Role of Cybersecurity in Accounting
Cybersecurity has always been a critical component of protecting financial data, but its role in accounting is expanding as the digital landscape becomes more complex. Traditional accounting practices are increasingly intertwined with digital systems, making cybersecurity an integral part of the accounting process.
How Cybersecurity Is Shaping Accounting:
- Integration of Cybersecurity in Accounting Practices: Cybersecurity measures are no longer just an IT concern; they are becoming embedded in accounting processes. This integration includes secure data storage, encrypted transactions, and the use of advanced authentication methods to protect financial records from unauthorized access.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Analytics: The future of accounting fraud prevention lies in real-time monitoring and advanced analytics. Cybersecurity tools equipped with machine learning algorithms can continuously monitor accounting transactions, flagging suspicious activities as they occur and allowing for immediate intervention.
- Collaboration Between IT and Finance Teams: As the line between accounting and cybersecurity blurs, collaboration between IT and finance teams is becoming essential. These teams must work together to develop and implement security protocols that protect financial data from both internal and external threats.
- Regulatory Compliance: As governments and regulatory bodies recognize the growing threat of accounting fraud, they are introducing more stringent cybersecurity regulations. Compliance with these regulations is becoming a key aspect of accounting practices, ensuring that financial data is protected and that organizations are prepared to respond to potential breaches.
Predictions for the Future of Accounting Fraud Prevention
Looking ahead, the landscape of accounting fraud prevention will be shaped by the continuous evolution of technology and the ongoing arms race between fraudsters and cybersecurity professionals. Organizations must stay ahead of these changes to protect themselves from increasingly sophisticated threats.
Key Predictions for the Future:
- Increased Adoption of AI and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning will play a pivotal role in detecting and preventing accounting fraud. These technologies will enable organizations to identify patterns and anomalies in financial data that could indicate fraudulent activities, allowing for more proactive fraud prevention.
- Blockchain as a Fraud Deterrent: As blockchain technology matures, it will become a more prominent tool in the fight against accounting fraud. The transparency and immutability of blockchain can help prevent the manipulation of financial records, making it harder for fraudsters to alter or falsify data.
- Greater Emphasis on Cybersecurity Education: Employee training and awareness will continue to be a critical component of cybersecurity strategies. Organizations will invest more in educating their employees about the latest threats and best practices for protecting financial data, reducing the risk of accounting fraud from within.
- Regulatory Evolution: As accounting fraud becomes more sophisticated, so too will the regulations designed to combat it. Governments and regulatory bodies will introduce new laws and guidelines that require businesses to adopt advanced cybersecurity measures and report potential fraud more transparently.
As we look to the future, it’s clear that the battle against accounting fraud will require a combination of cutting-edge technology, proactive cybersecurity measures, and ongoing education. By staying informed about emerging threats and evolving their strategies accordingly, organizations can protect themselves from the ever-present danger of accounting fraud.
Defending Against Deception: SearchInform’s Solutions for Combating Accounting Fraud
In the evolving landscape of digital threats and sophisticated fraud tactics, accounting fraud continues to pose a significant risk to organizations of all sizes. As we’ve explored in previous chapters, the integration of robust cybersecurity measures is crucial in protecting financial integrity. Enter SearchInform—a leader in cybersecurity and fraud prevention solutions, uniquely equipped to tackle the challenges of accounting fraud head-on. This section will explore how SearchInform’s tools and technologies provide comprehensive protection against accounting fraud, ensuring businesses remain resilient in the face of this ever-present threat.
Proactive Monitoring with SearchInform’s DLP Solutions
One of the core components of SearchInform’s arsenal against accounting fraud is its Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solution. In a world where sensitive financial information can easily be compromised, DLP tools play a pivotal role in preventing unauthorized access and data leakage.
How SearchInform’s DLP Protects Against Accounting Fraud:
- Real-Time Data Monitoring: SearchInform’s DLP solution continuously monitors data movement across the organization. By tracking how financial data is accessed, used, and transferred, it helps identify suspicious activities that could indicate accounting fraud.
- Granular Access Controls: The DLP system allows for precise control over who can access specific financial information. By limiting access to authorized personnel only, the risk of internal fraud is significantly reduced.
- Automated Alerts and Reporting: When potential threats or violations of data security policies are detected, the DLP solution triggers automated alerts, enabling swift response to mitigate risks. Detailed reports provide insights into the nature of the threat, allowing for informed decision-making.
Strengthening Incident Detection and Response
Accounting fraud often goes undetected until it’s too late, leading to substantial financial losses and reputational damage. SearchInform addresses this challenge with its advanced Incident Detection and Response (IDR) capabilities, designed to quickly identify and respond to fraudulent activities.
Key Features of SearchInform’s IDR Solution:
- Comprehensive Audit Trails: SearchInform’s IDR solution maintains detailed logs of all financial transactions and user activities. These audit trails are invaluable in tracing the origins of accounting fraud, allowing investigators to pinpoint exactly where and how the fraud occurred.
- Behavioral Analytics: By analyzing user behavior and financial patterns, the IDR system can detect anomalies that deviate from the norm, which may indicate fraudulent activities. This proactive approach enables the detection of fraud before it escalates.
- Rapid Response Mechanisms: When accounting fraud is detected, time is of the essence. SearchInform’s IDR solution is equipped with tools to facilitate immediate response actions, such as isolating compromised accounts or freezing suspicious transactions.
Enhancing Network Security for Financial Data
The security of the network infrastructure is fundamental in preventing accounting fraud, especially in an era where cyber threats are increasingly sophisticated. SearchInform’s network security solutions offer comprehensive protection for financial data, ensuring that fraudsters cannot exploit vulnerabilities within the system.
How SearchInform’s Network Security Solutions Combat Accounting Fraud:
- Advanced Threat Detection: SearchInform’s network security tools are designed to detect and neutralize advanced threats such as malware, phishing attempts, and unauthorized access. These tools provide a critical layer of defense against cyber attacks that could lead to accounting fraud.
- Encryption and Secure Data Transmission: To protect sensitive financial data during transmission, SearchInform employs robust encryption protocols. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be deciphered and misused by fraudsters.
- Network Segmentation and Access Control: By segmenting the network and implementing strict access controls, SearchInform’s solutions reduce the risk of accounting fraud by limiting the potential pathways through which unauthorized users can access financial systems.
Comprehensive Risk Management and Compliance
Preventing accounting fraud is not just about technology; it also involves managing risks and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. SearchInform’s solutions integrate risk management tools that help organizations identify vulnerabilities and stay compliant with financial regulations.
Risk Management with SearchInform:
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation: SearchInform provides tools for conducting thorough risk assessments, identifying areas where the organization may be vulnerable to accounting fraud. These insights enable the implementation of targeted mitigation strategies to reduce risk.
- Compliance Monitoring: Ensuring that financial practices align with regulatory requirements is crucial in preventing fraud. SearchInform’s compliance monitoring tools help organizations stay on top of regulatory changes and ensure that their financial processes meet the necessary standards.
- Incident Reporting and Documentation: In the event of an accounting fraud incident, SearchInform’s solutions facilitate comprehensive documentation and reporting, which are essential for legal and regulatory compliance.
The Future of Fraud Prevention with SearchInform
As accounting fraud continues to evolve, so too do the solutions offered by SearchInform. By staying at the forefront of technological advancements and continuously refining their tools, SearchInform ensures that organizations are well-equipped to combat the ever-changing landscape of accounting fraud.
Whether it’s through proactive monitoring, advanced incident response, or robust network security, SearchInform provides a comprehensive suite of solutions designed to protect against accounting fraud. For businesses looking to safeguard their financial integrity, SearchInform stands as a trusted partner in the ongoing battle against fraud.
Equip your organization with the tools it needs to combat accounting fraud effectively. Stay ahead of evolving threats by integrating SearchInform’s advanced cybersecurity solutions into your financial operations, ensuring your business remains secure and resilient.
Extend the range of addressed challenges with minimum effort
Company news
SearchInform uses four types of cookies as described below. You can decide which categories of cookies you wish to accept to improve your experience on our website. To learn more about the cookies we use on our site, please read our Cookie Policy.
Necessary Cookies
Always active. These cookies are essential to our website working effectively.
Cookies does not collect personal information. You can disable the cookie files
record
on the Internet Settings tab in your browser.
Functional Cookies
These cookies allow SearchInform to provide enhanced functionality and personalization, such as remembering the language you choose to interact with the website.
Performance Cookies
These cookies enable SearchInform to understand what information is the most valuable to you, so we can improve our services and website.
Third-party Cookies
These cookies are created by other resources to allow our website to embed content from other websites, for example, images, ads, and text.
Please enable Functional Cookies
You have disabled the Functional Cookies.
To complete the form and get in touch with us, you need to enable Functional Cookies.
Otherwise the form cannot be sent to us.

Subscribe to our newsletter and receive a bright and useful tutorial Explaining Information Security in 4 steps!

Subscribe to our newsletter and receive case studies in comics!







