What is Risk Retention?
- Introduction to Risk Retention
- Types of Risks Suitable for Retention
- Low-Probability but High-Impact Risks
- High-Probability but Low-Impact Risks
- Financial Risks and Operational Risks
- Strategic Risks Worth Retaining
- Situational Retention: When Context Matters
- Why Retaining Certain Risks Makes Sense
- Implementing Risk Retention
- Criteria for Deciding to Retain Risks
- The Role of Cost-Benefit Analysis
- Integration with Insurance Strategies
- Building Organizational Buy-In for Risk Retention
- Leveraging Technology for Effective Risk Retention
- Periodic Review and Adaptation
- Bridging to Benefits: The Rewards of Risk Retention
- Benefits of Risk Retention
- Financial Efficiency and Cost Savings
- Empowering Internal Risk Control Measures
- Greater Flexibility and Agility
- Recognizing the Other Side of Risk Retention
- Challenges and Limitations of Risk Retention
- Potential for Financial Strain
- SearchInform Risk Monitor provides tools for:
- Difficulty in Predicting Costs
- Resource Limitations
- Psychological Barriers to Retention
- Regulatory and Compliance Concerns
- Facing Challenges with Confidence
- Tools and Techniques for Risk Retention
- Importance of Data-Driven Decision-Making
- Risk Quantification and Modeling
- Role of Advanced Analytics
- Leveraging Real-Time Monitoring Systems
- Technology-Driven Collaboration
- Human Expertise Meets Technology
- Looking Ahead: Combining Strategy with Innovation
- Case Studies and Real-World Applications of Risk Retention
- Successful Risk Retention Strategies
- Lessons Learned from Risk Retention Failures
- Hybrid Approaches: Combining Retention with Complementary Strategies
- Real-World Takeaways: Lessons for Your Business
- SearchInform Solutions for Risk Retention
- Pinpointing Risks with Advanced Risk Assessment Tools
- Empowering Risk Retention with Real-Time Monitoring
- Seamless Integration with Existing Frameworks
- Your Risk Retention Strategy Starts Here
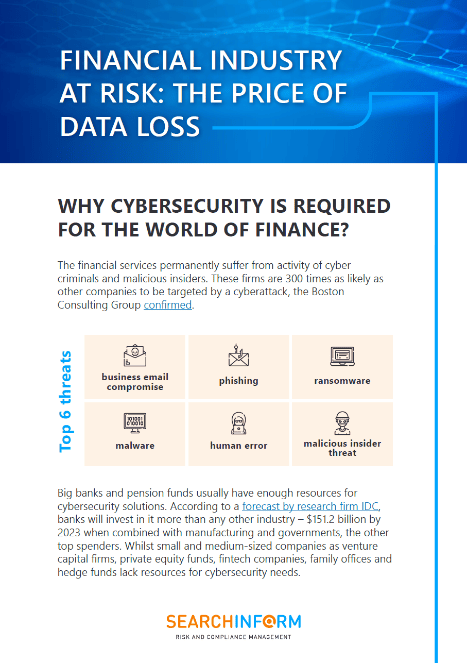
Introduction to Risk Retention
Imagine driving through an unpredictable storm. You see a pothole ahead—minor but unavoidable. You decide to navigate it yourself rather than calling for help. Now picture this scenario in the context of business. Risk retention operates on this principle: choosing to face certain risks directly instead of avoiding or transferring them. But why would any organization take risks head-on when they could pass them to someone else?
Risk retention isn’t recklessness—it’s a calculated strategy. It’s about owning manageable risks, preparing for their impact, and turning potential pitfalls into opportunities for growth. Unlike avoidance, where risks are sidestepped entirely, or transfer strategies like insurance, retention embraces uncertainties within your control. Understanding this strategy provides a fresh perspective on financial efficiency, resilience, and organizational autonomy.
Think of risk retention as a cornerstone of a proactive risk management approach—equipping businesses to face challenges head-on while keeping costs under control.
Types of Risks Suitable for Retention
Not all risks demand external intervention. Some can—and should—be handled internally. But how do you identify these risks? It’s about finding the sweet spot between likelihood and impact, balancing the scales of cost-effectiveness and control. Let’s uncover the types of risks that fit seamlessly into a risk retention strategy.
Low-Probability but High-Impact Risks
Think of a once-in-a-blue-moon event—a data server crash or a natural disaster affecting a satellite office. These risks don’t justify hefty insurance premiums due to their rarity. Yet, businesses can prepare by setting aside reserves or implementing proactive measures. For example, a tech startup might retain the risk of equipment damage but mitigate it through regular maintenance and backups.
High-Probability but Low-Impact Risks
These are the small, recurring ripples in the sea of operations—things like minor software bugs, routine equipment repairs, or brief staffing gaps. Handling these in-house makes sense; the cost of external coverage often outweighs the financial impact of the risks themselves. By retaining these risks, businesses streamline operations without unnecessary expenses.
Financial Risks and Operational Risks
Certain financial uncertainties, such as currency fluctuations or temporary dips in revenue, are predictable and manageable, making them prime candidates for risk retention. Similarly, operational risks like supply chain delays or seasonal demand fluctuations are often better absorbed internally, ensuring smooth and cost-efficient processes.
Strategic Risks Worth Retaining
Sometimes, retaining risk isn’t just practical—it’s strategic. Take innovative product launches: the uncertainty surrounding customer reception can’t always be transferred. Retaining this risk allows businesses to reap the rewards of bold moves, learning from setbacks while maintaining control over their vision.
Situational Retention: When Context Matters
Context often determines whether a risk is worth retaining. A manufacturing firm in a low-risk flood zone might forgo expensive flood insurance, relying instead on localized flood barriers. By understanding specific operational contexts, businesses can make smarter retention decisions.
Why Retaining Certain Risks Makes Sense
The decision to retain certain risks isn’t just about saving costs—it’s about agility and resilience. It empowers businesses to focus on what they can control while fostering innovation. But how do you ensure the right risks are retained? Stay tuned as we explore the practical steps for implementing a robust risk retention strategy.
Implementing Risk Retention
Risk retention is a deliberate and strategic choice, not an afterthought. It’s about deciding which risks your business can shoulder and preparing to handle them effectively. To implement risk retention successfully, you need a clear plan, robust tools, and a culture that embraces calculated risks. Let’s break it down step by step.
Criteria for Deciding to Retain Risks
How do you decide which risks are worth retaining? Start by assessing your business's ability to absorb potential losses without compromising core functions. Here are the key criteria to consider:
- Risk Tolerance: Understand your organization’s capacity to take on risk. For instance, a startup with limited reserves might retain fewer risks than an established corporation with diversified revenue streams.
- Historical Patterns: Analyze past incidents to identify predictable risks that can be managed internally. Historical data can often point to recurring, low-impact events that don’t require external coverage.
- Cost vs. Benefit: Weigh the financial implications of retaining versus transferring a risk. If the cost of transferring far exceeds the potential loss, retention may be the smarter option.
The Role of Cost-Benefit Analysis
Cost-benefit analysis is your guiding light in risk retention. By evaluating the financial impact of retaining a risk against the cost of mitigating or transferring it, you can make informed decisions.
For example:
- A midsize retail business might choose to retain the risk of minor shoplifting incidents, as investing in additional security or extensive insurance may outweigh the cost of these losses.
- A manufacturing firm may self-insure against minor equipment failures, using internal reserves rather than purchasing costly insurance coverage.
A well-executed analysis ensures that every dollar spent aligns with the business's risk tolerance and operational priorities.
Integration with Insurance Strategies
Risk retention and insurance are not mutually exclusive—they complement each other. A hybrid approach, combining internal risk management with strategic insurance coverage, offers the best of both worlds.
Key approaches include:
- Self-Insurance: Businesses create an internal fund to cover predictable risks, such as routine legal expenses or small-scale damages.
- Catastrophic Coverage: External insurance policies are reserved for low-probability, high-impact events, like natural disasters or large-scale cyberattacks.
- Layered Risk Management: By retaining manageable risks and insuring against catastrophic ones, companies achieve cost efficiency without compromising security.
This integration ensures resources are allocated wisely, covering risks that align with the business’s capacity to manage them.
Building Organizational Buy-In for Risk Retention
Implementing risk retention is not just a technical decision—it’s a cultural one. Employees at all levels need to understand the strategy and their role in its success. Here’s how to foster organizational alignment:
- Training Programs: Educate employees on the concept of risk retention, its benefits, and the specific risks being retained.
- Leadership Support: Ensure that leadership teams champion the strategy, demonstrating its alignment with broader business goals.
- Transparency: Clearly communicate why certain risks are retained and how the organization is prepared to manage them.
When employees see the value of risk retention, they’re more likely to support the strategy and contribute to its success.
Leveraging Technology for Effective Risk Retention
Technology is a game-changer in the realm of risk management. By harnessing advanced tools, businesses can streamline the process of retaining and managing risks effectively.
Innovative technologies include:
- Predictive Analytics: Use historical data to forecast potential risks and prepare mitigation strategies.
- Simulation Tools: Run "what-if" scenarios to test the impact of retained risks under different conditions, ensuring preparedness for unexpected events.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Employ data-driven dashboards that provide up-to-the-minute insights into risk exposure, helping businesses respond quickly and efficiently.
- Incident Management Systems: Automate the reporting and resolution of retained risks to reduce downtime and prevent escalation.
Integrating technology into your risk retention framework enhances accuracy, efficiency, and confidence in managing uncertainties.
Periodic Review and Adaptation
No risk retention strategy is set in stone. Businesses operate in dynamic environments where risks evolve over time. Regularly reviewing and adapting your strategy ensures it remains relevant and effective.
Key areas to review include:
- Emerging Risks: Stay ahead of new threats, such as evolving cyberattack methods or changing regulatory landscapes.
- Financial Health: Reassess your organization’s ability to absorb risks based on current financial performance.
- Lessons Learned: Analyze how retained risks were managed in past incidents to identify opportunities for improvement.
By keeping the strategy flexible and responsive, businesses can confidently navigate an ever-changing risk landscape.
Bridging to Benefits: The Rewards of Risk Retention
Implementing risk retention effectively sets the stage for tangible benefits. From cost savings to increased operational flexibility, this strategy empowers businesses to turn risks into opportunities. Curious about how embracing risk retention can transform your organization? Let’s explore the significant advantages of this approach in the next section.
Benefits of Risk Retention
Risk retention isn’t just a strategy—it’s a powerful tool that empowers organizations to operate with confidence and agility. By carefully choosing and managing which risks to retain, businesses can unlock a range of advantages that extend far beyond simple cost savings.
Financial Efficiency and Cost Savings
One of the most compelling reasons to embrace risk retention is its potential for financial efficiency. By avoiding the high costs of transferring certain risks to insurers, businesses can allocate their resources more strategically.
- Lower Insurance Premiums: Retaining manageable risks reduces reliance on external insurance, leading to significant cost savings.
- Predictable Costs: With self-insurance or reserve funds, businesses can predict and control their expenses, avoiding unexpected insurance rate hikes.
- Reinvestment Opportunities: The money saved from retaining risks can be reinvested into growth initiatives, such as product development or market expansion.
For example, a mid-sized logistics firm saved thousands annually by retaining the risk of minor vehicle damage, investing those savings into fleet upgrades instead.
Empowering Internal Risk Control Measures
Risk retention pushes businesses to strengthen their internal controls, leading to a more proactive and resilient risk management approach.
- Enhanced Preparedness: By retaining risks, organizations are motivated to develop robust response plans and contingency measures.
- Customized Solutions: Internal controls can be tailored to address the unique challenges of retained risks, offering greater flexibility than standardized insurance policies.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly managing retained risks fosters a culture of innovation and improvement within the organization.
Take the example of a manufacturing company that retained the risk of equipment downtime. By investing in predictive maintenance technology, they reduced overall downtime and improved operational efficiency.
Greater Flexibility and Agility
Retained risks offer businesses the flexibility to respond quickly and decisively without waiting for external insurers or third parties.
- Faster Decision-Making: With retained risks, businesses can act immediately, reducing delays caused by insurance claim processes.
- Freedom to Innovate: Retention encourages risk-taking in areas that drive innovation, such as launching new products or exploring emerging markets.
- Direct Control: Businesses retain full control over how risks are managed, avoiding the constraints of insurance contracts.
For instance, a tech startup retained the risk of server outages and invested in an in-house IT team. This approach allowed them to resolve issues faster and enhance their customer service reputation.
Recognizing the Other Side of Risk Retention
While the benefits of risk retention are clear and compelling, no strategy is without its hurdles. For every advantage, there are challenges that demand attention and preparation. Retaining risks involves a fine balance—managing potential gains while navigating the uncertainties. To fully harness its potential, businesses must also be ready to face the complexities that come with it.
Let’s explore the challenges and limitations that accompany this strategy and how they can shape an organization’s approach to risk retention.
Challenges and Limitations of Risk Retention
Risk retention offers significant advantages, but it’s not without its complexities. Balancing the benefits with the potential downsides requires careful planning, foresight, and agility. Let’s dive into the challenges organizations face when implementing risk retention and how they can turn obstacles into opportunities.
Potential for Financial Strain
Retaining risks can sometimes feel like walking a financial tightrope. While it saves money upfront by avoiding expensive insurance premiums, unexpected events can stretch resources thin.
- Surprise Crises: Imagine a restaurant chain retaining the risk of minor kitchen equipment failures, only to face simultaneous breakdowns at multiple locations. Without adequate reserves, such situations can disrupt operations and strain finances.
- Mitigating the Strain: Businesses must ensure their financial cushions are robust enough to absorb potential shocks. Setting aside contingency funds and regularly reviewing financial health are crucial steps to staying prepared.

Difficulty in Predicting Costs
Forecasting the financial impact of retained risks is as much an art as it is a science. Even with advanced tools, predicting the exact cost of risks can be challenging, leading to underfunded reserves or unanticipated losses.
- Evolving Risk Landscapes: Risks evolve. What seemed manageable last year—like minor cyber threats—can balloon into larger issues as attackers grow more sophisticated.
- Improving Cost Predictions: Leveraging historical data, advanced analytics, and predictive modeling can help businesses make more accurate forecasts. Regular risk assessments ensure organizations stay ahead of emerging threats.
Resource Limitations
Risk retention isn’t a passive activity; it requires active management, skilled personnel, and advanced tools. Smaller organizations, in particular, may find it difficult to allocate the necessary resources.
- Knowledge Gaps: Retaining risks like legal disputes or cybersecurity incidents demands specialized knowledge, which may not always be available in-house.
- Technology Deficits: Without tools like real-time monitoring systems or risk management software, businesses risk inefficiencies or delayed responses.
- Bridging the Gap: Outsourcing expertise, investing in employee training, and adopting scalable technology solutions can mitigate these limitations.
Psychological Barriers to Retention
Sometimes, the biggest hurdle is mindset. Risk retention requires organizations to embrace uncertainties, which can be uncomfortable, especially in risk-averse cultures.
- Fear of Failure: Retaining risks means accepting potential downsides, which can be daunting for leadership teams focused on avoiding negative outcomes.
- Building Confidence: Transparent communication about the rationale and benefits of risk retention, paired with consistent successes in managing retained risks, can shift organizational culture toward calculated boldness.
Regulatory and Compliance Concerns
In some industries, regulations can limit how risks are retained, adding another layer of complexity to the strategy.
- Industry-Specific Rules: Financial institutions, for instance, may face restrictions on retaining certain risks due to regulatory oversight.
- Staying Compliant: Regular legal consultations and compliance audits ensure that risk retention strategies align with industry standards and regulations.
Facing Challenges with Confidence
Every challenge brings an opportunity to innovate and grow. By addressing these hurdles proactively—whether through financial planning, advanced analytics, or cultural shifts—businesses can turn the limitations of risk retention into strengths. The next step? Understanding the tools and techniques that make overcoming these challenges not just possible, but seamless. Let’s explore how technology and data-driven strategies can redefine the way organizations approach risk retention.
Tools and Techniques for Risk Retention
Risk retention isn’t just about making decisions—it’s about making the right decisions. And to do that, businesses need the right tools and techniques. With a data-driven approach, advanced technologies, and innovative methodologies, managing retained risks becomes less of a gamble and more of a calculated strategy. Let’s explore how these tools and techniques can transform risk retention into a cornerstone of effective risk management.
Importance of Data-Driven Decision-Making
In the age of information, data is king. Businesses that leverage data-driven decision-making are better equipped to identify, evaluate, and manage retained risks.
- Turning Data into Insights: Historical data, industry benchmarks, and real-time metrics help organizations understand the likelihood and impact of various risks.
- Informed Choices: Instead of relying on gut instincts, businesses can use hard evidence to decide which risks to retain, ensuring alignment with financial and operational goals.
- Dynamic Adjustments: Continuous monitoring of risk indicators allows businesses to adapt strategies as conditions evolve, minimizing surprises.
Risk Quantification and Modeling
You can’t manage what you can’t measure. Risk quantification and modeling enable organizations to assign tangible values to abstract uncertainties, making them easier to handle.
- Scenario Planning: Modeling tools simulate "what-if" scenarios, predicting how different risks might impact operations. For example, a retail chain could model the effects of seasonal supply chain delays.
- Risk Heat Maps: Visualization tools help prioritize risks by mapping their probability and potential impact, providing a clear picture of where to focus retention efforts.
- Financial Projections: Quantifying potential costs ensures that retained risks align with the organization’s financial capacity.
Role of Advanced Analytics
Advanced analytics goes beyond data collection—it helps businesses uncover patterns, predict outcomes, and act proactively.
- Predictive Analytics: Identify trends and emerging risks before they escalate. For instance, a bank might use predictive models to detect patterns in fraud attempts, retaining low-level risks while addressing high-impact ones.
- Prescriptive Analytics: Suggest actionable steps for managing retained risks, offering recommendations tailored to specific scenarios.
- Machine Learning Models: Continuously refine risk predictions by learning from historical data, improving accuracy over time.
Leveraging Real-Time Monitoring Systems
Risk retention thrives on timely insights. Real-time monitoring systems ensure businesses stay ahead of the curve.
- Immediate Alerts: Identify anomalies or emerging threats as they happen, enabling swift responses.
- Integrated Dashboards: Provide a unified view of all retained risks, helping decision-makers assess the organization’s overall risk posture at a glance.
- Automated Reporting: Streamline risk assessments with automated updates, ensuring that leadership teams have up-to-date information at all times.
Technology-Driven Collaboration
Collaboration tools enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of managing retained risks, especially in larger organizations.
- Cloud-Based Platforms: Facilitate information sharing and decision-making across departments, ensuring a unified approach to risk management.
- AI-Powered Solutions: Assist teams in prioritizing risks, generating insights, and automating routine tasks related to risk retention.
- Cross-Functional Teams: Foster collaboration between finance, operations, and IT teams, ensuring all perspectives are considered when retaining risks.
Human Expertise Meets Technology
While tools and analytics are invaluable, human expertise remains a vital element in risk retention. Combining the two ensures a balanced approach:
- Expert Oversight: Risk managers bring contextual understanding and strategic insights that technology alone cannot provide.
- Augmented Decision-Making: Tools enhance human decision-making by providing actionable data and eliminating guesswork.
- Continuous Learning: Teams equipped with both expertise and technology can adapt to evolving risks with agility.
Looking Ahead: Combining Strategy with Innovation
With the right tools and techniques, risk retention becomes more than just a strategy—it becomes a competitive advantage. But what does this look like in the real world? In the next section, we’ll explore real-life applications of risk retention, including success stories and lessons learned from failures. Ready to see how theory translates into practice? Let’s dive in!
Case Studies and Real-World Applications of Risk Retention
Risk retention is more than just a theory; it’s a dynamic strategy with real-world implications. By looking at successful applications and cautionary tales, we can better understand its power and pitfalls. From innovative solutions to hard-earned lessons, these examples highlight how businesses across industries approach retained risks—and what you can learn from them.
Successful Risk Retention Strategies
When done right, risk retention becomes a tool for cost savings, operational efficiency, and innovation. Here’s how organizations have harnessed its potential:
-
E-Commerce Leader Turns Outages Into Opportunities
A global e-commerce company faced frequent system outages due to traffic surges during sales events. Instead of outsourcing IT solutions or purchasing expensive insurance, they retained the risk and invested in advanced load-balancing technologies and real-time monitoring systems. This proactive approach not only saved millions in premiums but also ensured faster recovery times, keeping customer satisfaction high. -
Retail Chain Reimagines Loss Prevention
A mid-sized retail chain decided to retain the risk of minor inventory shrinkage due to shoplifting. They redirected funds typically spent on insurance premiums into employee training, better store layouts, and enhanced monitoring systems. Over three years, their approach led to a 25% reduction in theft and significant cost savings, proving that internal solutions can outperform external coverage. -
Construction Firm Builds Resilience Against Delays
A large construction company retained the risk of minor supply chain delays, which are common in the industry. Instead of insuring against disruptions, they diversified their supplier base and established robust relationships with multiple vendors. This strategy allowed them to navigate disruptions with minimal financial impact while maintaining project timelines. -
Healthcare Provider Embraces Predictable Risks
A healthcare organization retained the risk of minor equipment failures, using predictive analytics to monitor and maintain devices proactively. By investing in internal maintenance teams and scheduling regular checks, they minimized downtime and avoided the hefty costs associated with third-party service contracts.
Lessons Learned from Risk Retention Failures
When risk retention is poorly executed, the results can be costly. These cautionary tales reveal the importance of planning, monitoring, and understanding the full scope of retained risks:
-
Retailer’s Supply Chain Shortfall
A national retail chain underestimated the potential impact of retained supply chain risks during a natural disaster. Lacking robust contingency plans, they faced severe inventory shortages, resulting in millions in lost revenue and damage to customer trust. The oversight highlighted the need for predictive analytics and scenario planning in risk retention strategies. -
Cybersecurity Gaps in Manufacturing
A small manufacturing company retained the risk of minor cyber incidents, believing their in-house IT team could handle potential threats. However, when a ransomware attack occurred, they lacked the tools and expertise to mitigate the damage. The downtime and recovery costs exceeded their projections, emphasizing the need for a balanced approach to retention and external support. -
Underfunded Reserves in Healthcare
A healthcare provider retained the risk of small malpractice claims, relying on historical data to forecast expenses. When claims unexpectedly spiked due to changing regulations, their reserves were insufficient, forcing budget cuts in critical areas like staffing and equipment upgrades. The incident underscored the importance of adaptability in financial planning for retained risks.
Hybrid Approaches: Combining Retention with Complementary Strategies
Sometimes, the best results come from blending risk retention with other risk management techniques. Hybrid strategies allow businesses to retain manageable risks while transferring high-impact uncertainties, creating a balanced and resilient approach.
-
Tech Firm’s Balanced Risk Portfolio
A technology company retained the risk of minor hardware theft while insuring against catastrophic data breaches. This dual approach allowed them to save on insurance costs while ensuring protection against large-scale threats. By aligning their strategy with risk tolerance, they achieved both financial efficiency and robust security. -
Hospital Optimizes Risk Management with Predictive Tools
A hospital retained the risk of minor equipment failures, using predictive maintenance software to anticipate and address issues before they escalated. Simultaneously, they insured against high-impact risks like malpractice claims. This hybrid approach reduced operational costs and safeguarded against severe financial losses. -
Logistics Company Navigates Weather-Related Risks
A logistics company retained the risk of minor weather delays, equipping its fleet with GPS tracking and real-time route optimization technology. For major disruptions like hurricanes, they maintained insurance coverage. This strategy ensured efficiency during routine operations and protection during extreme events.
Real-World Takeaways: Lessons for Your Business
These case studies show that risk retention, when executed thoughtfully, can lead to significant savings, operational improvements, and greater control. However, they also highlight the potential pitfalls of underestimating risks or failing to plan adequately. The key lies in balancing retention with robust internal controls, advanced technologies, and external support when necessary.
But how can your business ensure it’s on the winning side of this equation? The answer lies in leveraging cutting-edge tools and expert solutions. In the next section, we’ll explore how SearchInform’s technologies and services can help you take your risk retention strategy to the next level. Let’s see how you can turn risks into opportunities!
SearchInform Solutions for Risk Retention
Managing retained risks effectively requires precision, foresight, and the right tools. SearchInform provides businesses with cutting-edge solutions that take the guesswork out of risk retention. From identifying risks worth retaining to managing them seamlessly, SearchInform empowers organizations to transform risk into opportunity. Let’s explore how SearchInform’s tools and expertise redefine risk retention.
Pinpointing Risks with Advanced Risk Assessment Tools
Effective risk retention starts with understanding which risks are manageable and worth retaining. SearchInform’s risk assessment tools provide businesses with a clear picture of their risk landscape.
- Comprehensive Analysis: Using advanced analytics, SearchInform evaluates risks based on their likelihood, impact, and manageability, helping businesses decide whether to retain or mitigate.
- Tailored Insights: Unlike one-size-fits-all solutions, SearchInform delivers industry-specific risk insights, ensuring relevance and precision. Whether it’s operational risks in manufacturing or cybersecurity threats in financial services, SearchInform adapts to your unique needs.
- Proactive Identification: Spot emerging risks before they escalate. SearchInform’s tools use predictive analytics to highlight vulnerabilities, giving businesses the confidence to retain risks with full awareness of potential outcomes.
Empowering Risk Retention with Real-Time Monitoring
Retaining risks isn’t about passively hoping for the best—it’s about staying vigilant and prepared. SearchInform’s real-time monitoring systems make managing retained risks a proactive, streamlined process.
- Live Alerts: Stay ahead of the curve with instant notifications for any anomalies or events related to retained risks. This enables businesses to act quickly, minimizing potential fallout.
- Integrated Dashboards: SearchInform’s dashboards consolidate all risk data into one intuitive interface. Decision-makers can monitor retained risks, financial reserves, and mitigation efforts at a glance, ensuring no detail is overlooked.
- Automation for Efficiency: Automate routine risk tracking and reporting tasks, freeing up time and resources for strategic decision-making.
Seamless Integration with Existing Frameworks
No business operates in isolation, and neither should your risk management tools. SearchInform’s solutions integrate seamlessly into your existing systems, enhancing the effectiveness of your overall risk management strategy.
- Compatibility Across Platforms: Whether you use legacy systems or cutting-edge platforms, SearchInform’s tools are designed to integrate effortlessly, minimizing disruptions and maximizing efficiency.
- Holistic Risk Management: From incident detection to ongoing evaluation, SearchInform works across the entire risk management lifecycle, ensuring retained risks are managed in harmony with other strategies.
- Scalable Solutions: As your business grows, SearchInform’s tools scale with you, providing consistent support no matter the size or complexity of your organization.
Your Risk Retention Strategy Starts Here
Why let uncertainty dictate your decisions when you can take control? With SearchInform, you gain the tools, insights, and confidence to master risk retention. Identify the risks worth taking, manage them with precision, and turn them into opportunities for growth.
Take the first step toward smarter risk retention today. Explore SearchInform’s solutions and see how we can help your business thrive in the face of uncertainty.
Full-featured software with no restrictions
on users or functionality
Company news
SearchInform uses four types of cookies as described below. You can decide which categories of cookies you wish to accept to improve your experience on our website. To learn more about the cookies we use on our site, please read our Cookie Policy.
Necessary Cookies
Always active. These cookies are essential to our website working effectively.
Cookies does not collect personal information. You can disable the cookie files
record
on the Internet Settings tab in your browser.
Functional Cookies
These cookies allow SearchInform to provide enhanced functionality and personalization, such as remembering the language you choose to interact with the website.
Performance Cookies
These cookies enable SearchInform to understand what information is the most valuable to you, so we can improve our services and website.
Third-party Cookies
These cookies are created by other resources to allow our website to embed content from other websites, for example, images, ads, and text.
Please enable Functional Cookies
You have disabled the Functional Cookies.
To complete the form and get in touch with us, you need to enable Functional Cookies.
Otherwise the form cannot be sent to us.

Subscribe to our newsletter and receive a bright and useful tutorial Explaining Information Security in 4 steps!

Subscribe to our newsletter and receive case studies in comics!







